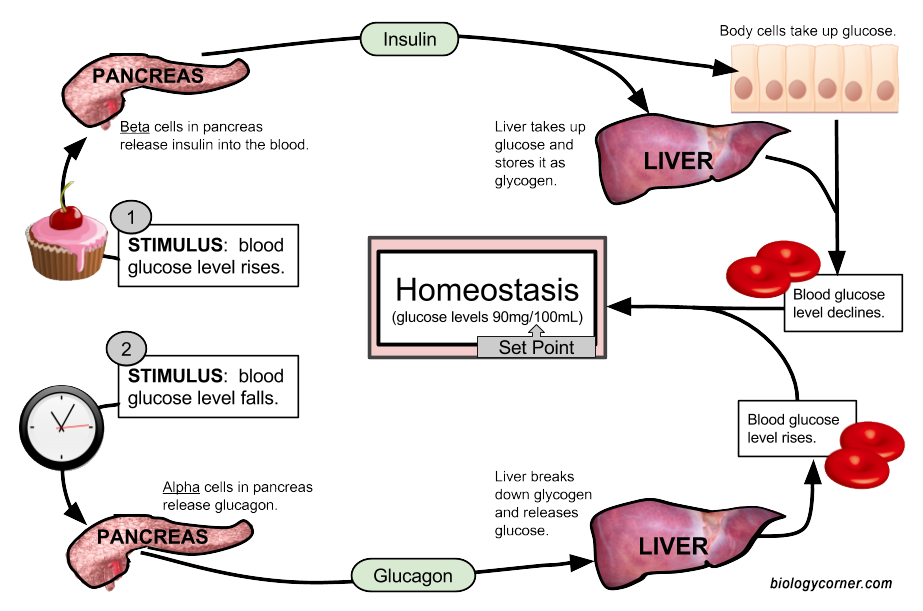
Diagram Blood Glucose . Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. The control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change. Central to maintaining blood glucose homeostasis are two hormones, insulin and glucagon, both produced by the pancreas and released into the. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. Glucose is central to energy consumption.
from truevaluedentalinstitute.in
The control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change. Central to maintaining blood glucose homeostasis are two hormones, insulin and glucagon, both produced by the pancreas and released into the. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. Glucose is central to energy consumption. The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause.
Role of Hormones in Homeostasis of Blood Glucose Levels True value
Diagram Blood Glucose Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Central to maintaining blood glucose homeostasis are two hormones, insulin and glucagon, both produced by the pancreas and released into the. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. The control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change.
From www.shutterstock.com
312 Good Blood Flow Images, Stock Photos & Vectors Shutterstock Diagram Blood Glucose Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From truevaluedentalinstitute.in
Role of Hormones in Homeostasis of Blood Glucose Levels True value Diagram Blood Glucose Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. Central to maintaining blood glucose homeostasis are two hormones, insulin and glucagon, both produced by the pancreas and released into the.. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Normal Level Of Blood Glucose Diagram Diagram Blood Glucose When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From naturalhealthconnections.com.au
Blood Sugar Spikes Diagram Natural Health Connections Diagram Blood Glucose Glucose is central to energy consumption. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. The control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.frontiersin.org
Frontiers Origins and History of the Minimal Model of Glucose Regulation Diagram Blood Glucose Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. Glucose is central to energy consumption. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change. The control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.shalom-education.com
Controlling Blood Glucose Concentration GCSE Biology Revision Diagram Blood Glucose 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause. The control of blood sugar (glucose). Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.researchgate.net
Mechanism of maintaining desired blood glucose levels Download Diagram Blood Glucose Glucose is central to energy consumption. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From mediscanlab.com
GlucoseBlood MediScan Lab Diagram Blood Glucose The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause. Central to maintaining blood glucose homeostasis are two hormones, insulin and glucagon, both produced by the pancreas and released into the. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change. 13 rows. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.cmihealth.com
What Your Blood Glucose Test Results Mean CMI Health Blog Diagram Blood Glucose Central to maintaining blood glucose homeostasis are two hormones, insulin and glucagon, both produced by the pancreas and released into the. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. Glucose is central to energy consumption. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.shalom-education.com
The Pancreas and Insulin Controlling Blood Glucose Shalom Education Diagram Blood Glucose The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. Glucose is central to energy consumption. The control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism.. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.tes.com
AQA GCSE Biology Control of blood glucose levels Teaching Resources Diagram Blood Glucose The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From melissa-bogspotrhodes.blogspot.com
Describe the Role of Insulin in Regulating Blood Sugar Levels Diagram Blood Glucose Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. The control of blood sugar (glucose) by. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.breathewellbeing.in
Blood Sugar Levels How Glucose Levels Affect Your Body? Breathe Well Diagram Blood Glucose The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause. The control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. When. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.dreamstime.com
Blood glucose level stock illustration. Illustration of laboratory Diagram Blood Glucose 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. Glucose is central to energy consumption. The control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.dreamstime.com
Glucose Levels in the Blood Diagram Stock Vector Illustration of Diagram Blood Glucose Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.alamy.com
Diagram illustrating Type 2 diabetes versus healthy blood glucose Diagram Blood Glucose The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels rise above normal in the top half of the diagram and how a hormone can cause. 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. The control of blood sugar (glucose). Diagram Blood Glucose.
From www.shutterstock.com
Blood Glucose Chart Stock Vector 766795750 Shutterstock Diagram Blood Glucose Central to maintaining blood glucose homeostasis are two hormones, insulin and glucagon, both produced by the pancreas and released into the. Carbohydrates and proteins ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. The loop shows us what happens. Diagram Blood Glucose.
From healthjade.net
Blood sugar regulation & hormone that regulates blood sugar Diagram Blood Glucose 13 rows blood sugar regulation is the process by which the levels of blood sugar, the common name for glucose dissolved in blood plasma, are maintained by the. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every organism worldwide and are. The loop shows us what happens when blood glucose levels. Diagram Blood Glucose.